The sun, a giant ball of burning gas millions of miles away, provides our planet with the light and warmth necessary for life. But did you know we can also harness its energy to power our homes, businesses, and even entire cities? Solar energy is a clean, renewable source of power that’s rapidly changing the way we generate electricity. Let’s dive deep into the fascinating world of solar energy and explore how this technology works.
The Photovoltaic Effect: The Heart of Solar Power
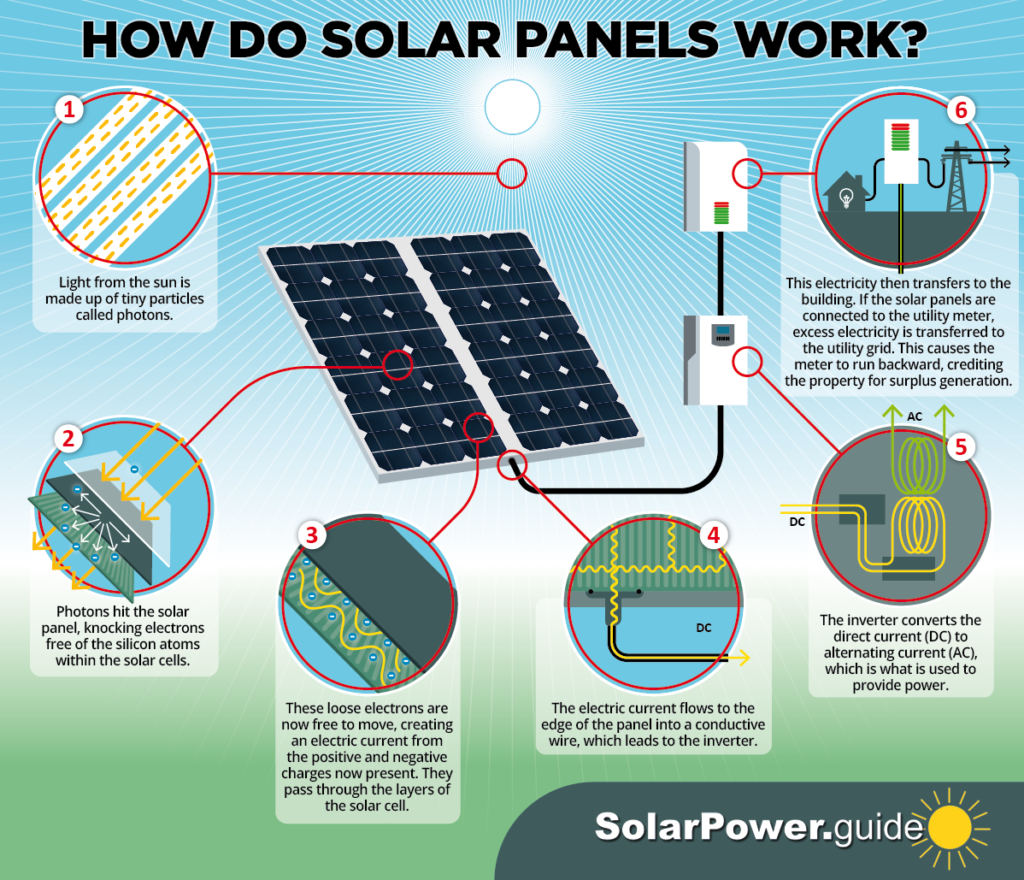
The journey from sunlight to electricity begins with a remarkable phenomenon known as the photovoltaic effect. This process, discovered in the 19th century, is the foundation of solar energy technology. It involves converting light energy directly into electrical energy using special materials called semiconductors.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the photovoltaic effect:
- Photons at Work: Sunlight is composed of tiny packets of energy called photons. When these photons strike a semiconductor material, such as silicon, they transfer their energy to the electrons within the material.
- Electrons Get Excited: The absorbed energy excites the electrons, causing them to break free from their atoms and become mobile.
- Creating an Electric Field: Semiconductor materials used in solar cells are specially designed with a built-in electric field. This field acts like an invisible guide, directing the flow of freed electrons in a specific direction.
- Generating Current: This organized movement of electrons is what we know as electric current. The solar cell generates direct current (DC) electricity, which can then be converted into alternating current (AC) electricity for use in our homes and businesses.
Solar Cells: The Building Blocks of Solar Panels
The devices that harness the photovoltaic effect are called solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells. These cells are typically made of silicon, a readily available element found in sand. To enhance their efficiency, solar cells are carefully engineered with various layers and materials to maximize light absorption and electron flow.
Key components of a typical solar cell include:
- Silicon layers: Form the core of the cell, where the photovoltaic effect takes place. These layers are doped with impurities to create an electric field.
- Anti-reflective coating: Minimizes light reflection, ensuring maximum absorption by the silicon layers.
- Metal contacts: Collect the generated electric current and transfer it to external wires.
- Encapsulation: Protects the delicate cell from environmental factors such as moisture and dust.
From Cells to Panels to Arrays: Scaling Up Solar Power
Individual solar cells are relatively small and generate a limited amount of power. To produce usable amounts of electricity, they are interconnected and assembled into larger units called solar panels, also known as photovoltaic modules.
- Solar panels: Consist of multiple solar cells wired together in series and parallel configurations to increase voltage and current output. They are typically encased in a protective frame with a glass front sheet for durability and weather resistance.
- Solar arrays: To further increase power output, multiple solar panels are connected together to form arrays. These arrays can range in size from small residential rooftop systems to massive utility-scale solar farms spanning acres of land.
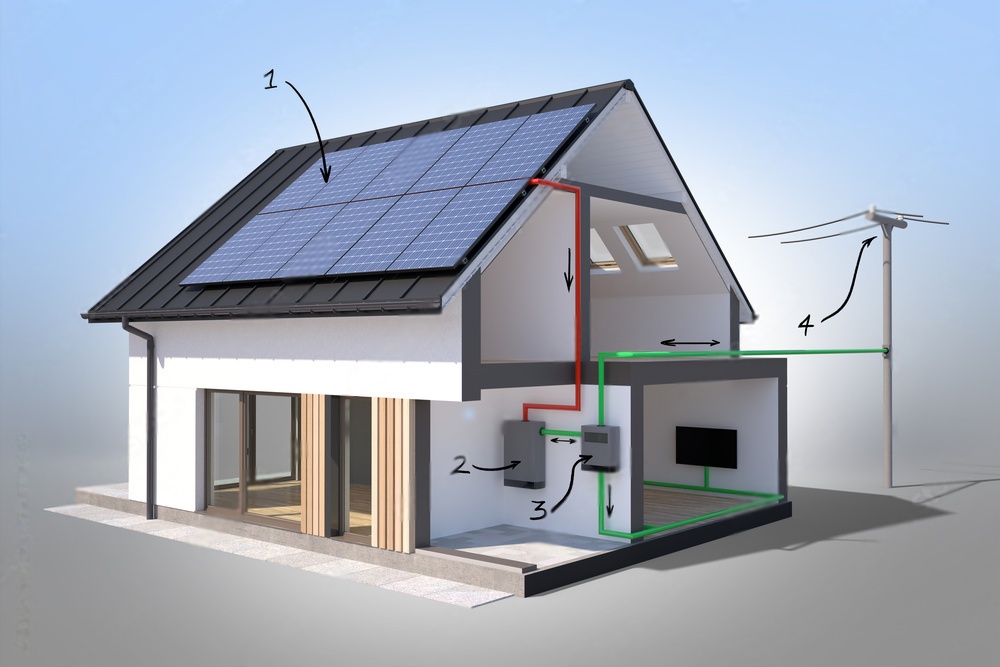
The Solar Energy System: More Than Just Panels
While solar panels are the most visible part of a solar energy system, several other components work together to capture, convert, and utilize the sun’s energy effectively.
- Inverter: The electricity generated by solar panels is in the form of direct current (DC). However, most household appliances and the electrical grid operate on alternating current (AC). The inverter acts as a converter, transforming DC electricity from the panels into AC electricity.
- Metering equipment: Meters track the amount of electricity produced by the solar panels and the amount consumed by the home or business. This information helps monitor system performance and calculate energy savings.
- Wiring and connections: A network of wires and connectors safely and efficiently transmit electricity between the solar panels, inverter, metering equipment, and the electrical system of the building.
- Mounting system: A sturdy mounting system securely attaches the solar panels to the roof or ground, ensuring they can withstand wind, snow, and other environmental conditions.
Types of Solar Energy Systems: Grid-Tied and Off-Grid
Solar energy systems can be broadly classified into two main types:
- Grid-connected systems: These systems are connected to the existing electrical grid. They can feed excess electricity back into the grid, often earning credits from the utility company, or draw electricity from the grid when solar production is low, such as at night or during cloudy weather.
- Off-grid systems: These systems operate independently of the electrical grid. They rely on batteries to store excess electricity generated during the day for use when the sun is not shining. Off-grid systems are often used in remote locations or for applications where grid connection is not feasible or desirable.
Applications of Solar Energy: Powering Our World
Solar energy’s versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, including:
- Residential: Powering homes, heating water, and even cooling homes with solar-powered air conditioning.
- Commercial: Providing electricity for businesses, reducing energy costs and carbon footprint.
- Industrial: Generating power for manufacturing processes and other industrial applications.
- Utility-scale: Large-scale solar farms that generate electricity for entire communities.
- Transportation: Powering electric vehicles and charging stations.
- Agriculture: Providing electricity for irrigation systems, livestock facilities, and other agricultural needs.
- Space exploration: Solar panels are used to power satellites and spacecraft, providing a reliable source of energy in the harsh environment of space.
Benefits of Solar Energy: A Sustainable Choice
Solar energy offers numerous benefits, making it an increasingly attractive option for individuals, businesses, and governments:
- Renewable and sustainable: Solar energy is a clean and abundant source of energy that does not produce greenhouse gas emissions or other pollutants, contributing to a healthier environment and mitigating climate change.
- Cost-effective: The cost of solar energy has decreased significantly in recent years, making it a competitive option compared to traditional fossil fuels. Government incentives and tax credits further enhance its affordability.
- Energy independence: Solar energy can reduce reliance on foreign oil and fossil fuels, promoting energy security and independence for individuals, communities, and nations.
- Job creation: The solar industry is a growing sector that creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research, contributing to economic growth and development.
- Reliable and low-maintenance: Solar panels have no moving parts, making them relatively low-maintenance and long-lasting. They typically come with warranties of 25 years or more.
- Versatile and adaptable: Solar panels can be installed on rooftops, ground-mounted, or even integrated into building materials, making them adaptable to various environments and applications.
The Future of Solar Energy: A Bright Outlook
Solar energy is poised to play a crucial role in the future of energy. Advancements in technology, coupled with decreasing costs, are making solar energy more accessible and efficient than ever before.
- Increased efficiency: Researchers are constantly developing new materials and techniques to improve the efficiency of solar cells, capturing more sunlight and generating more electricity.
- Energy storage: Advances in battery technology are making it easier and more affordable to store excess solar energy for use when the sun is not shining, enhancing the reliability and value of solar power systems.
- Smart grids: Integration of solar energy with smart grids allows for better management of electricity supply and demand, optimizing the use of renewable energy sources and improving grid stability.
- Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV): Solar panels are being increasingly integrated into building materials such as roofing tiles, windows, and facades, creating aesthetically pleasing and functional building designs.
As research and development continue, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of solar energy in the years to come, further solidifying its position as a leading source of clean and sustainable power.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of the Sun
Solar energy is a powerful and versatile technology that harnesses the sun’s energy to generate clean electricity and heat. With its numerous benefits and growing affordability, solar energy is transforming the way we power our world and paving the way for a sustainable energy future. By embracing the power of the sun, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, protect our environment, and create a brighter future for generations to come.
Helpful links : https://solarpower.guide/solar-energy-insights/how-do-solar-panels-work